
Write information for processes whose process ID numbers are given in proclist. Multiple -o options can be specified the format specification shall be interpreted as the -separated concatenation of all the format option-arguments. This is fully described in the STDOUT section. Write information according to the format specification given in format. The name of the default file and the format of a namelist file are unspecified. Specify the name of an alternative system namelist file in place of the default. (See STDOUT for the contents of a long listing.) The application shall ensure that the grouplist is a single argument in the form of a or -separated list. Write information for processes whose real group ID numbers are given in grouplist. Write information for processes whose session leaders are given in grouplist.
#What ps ef command in linux does full#
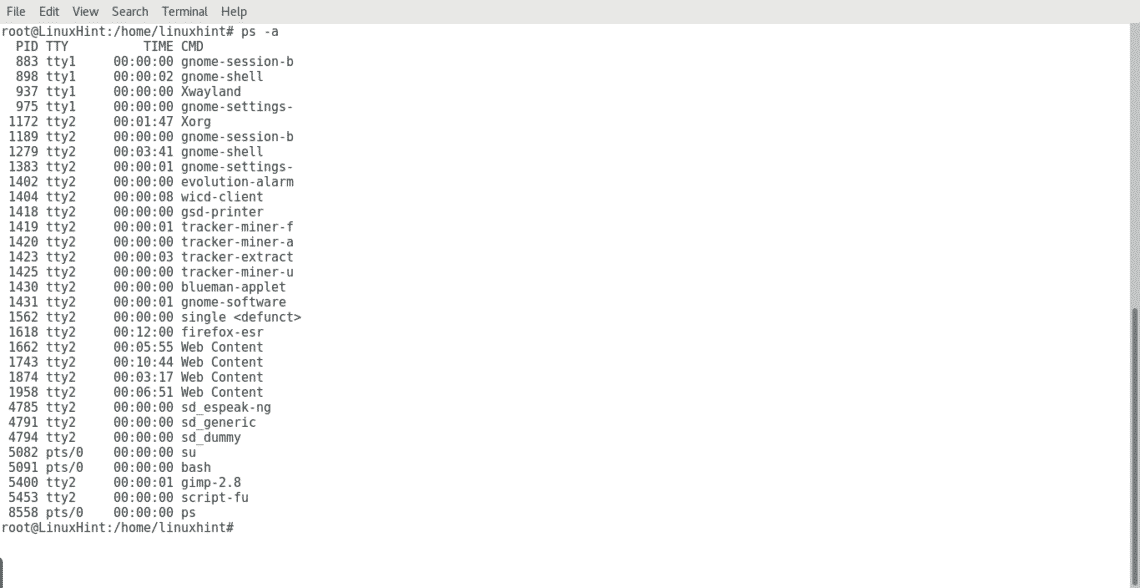
(See the STDOUT section for the contents of a full listing.) Write information for all processes, except session leaders. Implementations may omit session leaders from this list. Write information for all processes associated with terminals. Ps provides numerous options for manipulating the output according to our need.
proc contains virtual files, which is the reason it’s referred as a virtual file system. It reads the process information from the virtual files in /proc file-system. The ps command is used to list the currently running processes and their PIDs along with some other information, which depends on different options. Linux provides a utility called ps (which stands as abbreviation for “Process Status ”) for viewing information related with the processes on a system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
